March 31, 2016 - An invited review article entitled “Stabilizing nanostructures in metals using grain and twin boundary architectures” (Nature Reviews Materials, 1, 16019 (2016)) by Prof. K. Lu was published online in the inaugural volume of Nature Reviews Materials. Nature Review Materials is the first physical sciences Reviews journal at Nature launched in 2016, which publishes Reviews and Perspectives within materials science.
Forming alloys with impurity elements is a routine method for modifying the properties of metals. An alternative approach involves the incorporation of interfaces into the crystalline lattice to enhance the metal’s properties without changing its chemical composition. The introduction of high-density interfaces in nanostructured materials results in greatly improved strength and hardness; however, interfaces at the nanoscale show low stability. In this Review, Prof. Lu discussed recent developments in the stabilization of nanostructured metals by modifying the architectures of their interfaces. The amount, structure and distribution of several types of interfaces, such as high- and low-angle grain boundaries and twin boundaries, are discussed. He surveyed several examples of materials with nanotwinned and nanolaminated structures, as well as with gradient nanostructures, describing the techniques used to produce such samples and tracing their exceptional performances back to the nanoscale architectures of their interfaces.
Link: http://www.nature.com/articles/natrevmats201619
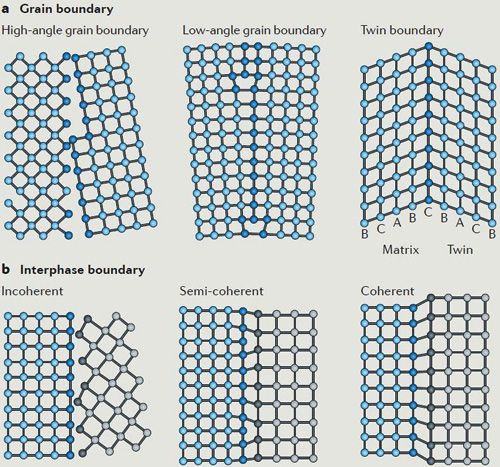
Figure 1. Grain boundary and interphase boundary.