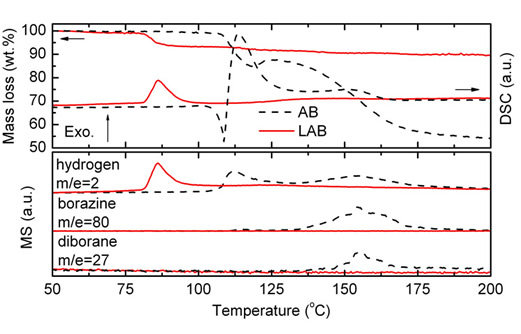
One of the major obstacles to the widespread use of the hydrogen as an energy carrier, especially for transportation applications, is the lack of the safe and efficient means for hydrogen storage. Ammonia borane (NH3BH3, AB) is an intriguing molecular solid with extremely high hydrogen capacity (19.6 wt.%) and favorable thermal stability. Much recent efforts have been directed to explore its potential for high-capacity hydrogen storage, but were frustrated by the sluggish thermolysis kinetics at ≿00 oC and the concurrent release of volatile by-products (e.g. borazine, diborane) that are detrimental for fuel cell operation. Recently, we demonstrate that mechanical milling 1:1 ammonia borane/lithium hydride mixture yields a destabilized hydrogen storage material--lithium amidoborane (LiNH2BH3, LAB) with a H-capacity of around 10 wt%, which is higher than the 2015 DOE gravimetric H-capacity target. Importantly, the material possesses satisfactory air-stability and can rapidly release over 7 wt% pure hydrogen at around 100 oC. These combined advantages make LAB material very promising for providing high-capacity on-board hydrogen source for transportation applications (see X.D. Kang, et al., Adv. Mater., 20(2008)2756).