Abradable seal coatings (ASCs), as the critical component for the aircraft turbine engines, are typically employed to minimize the clearance between the blade tip and the shroud, which consequently enhance aero-engine efficiency. However, high-performance and long-duration operation of ASCs is still limited by both corrosion and mechanical degradation.
The research team led by Prof. LI Ying from Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IMR, CAS) fabricated a high-performance CuAl-Ni/C ASC applied at the high-temperature and corrosive marine environment by using thermal spraying technology. This work was published in Chemical Engineering Journal.
Herein, a CuAl-Ni/C ASC system was developed by replacing part of Al with Cu based on Al-BN ASC system, which displays an excellent combination of high erosion resistance, sufficient abradability and anti-oxidation at high temperature. The superior anti-corrosion performance of the coating was proved to be derived from preferential corrosion of intermetallic compound AlCu4 in the coating, effectively suppressing corrosion of the coating. More importantly, the results display that the higher dissolution rate of Cu than Al during the initial stage of corrosion, which is inconsistent with the conventional perception that the activity of Al is significantly higher than that of Cu. The theoretical calculations further reveal inconsistency and unravel phenomenon resulted from preferential corrosion of AlCu4 in the coating.
This study not only paves a new avenue for the design of the high-performance ASCs at the high-temperature and corrosive marine environment, but also illuminates underlying mechanism of the corrosion of the CuAl-Ni/C ASC from atomic level, which is highly valued to guide future study on corrosion of multiphase system.
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
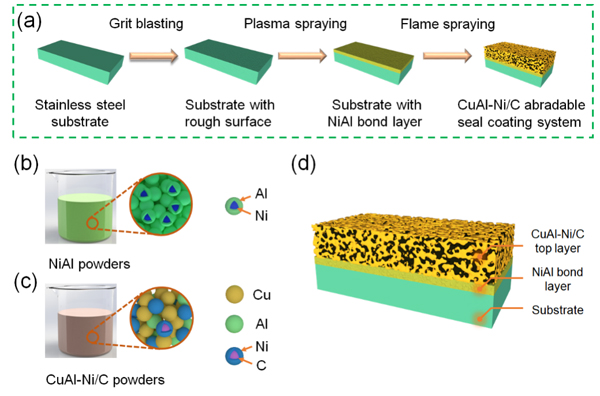
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of (a) the preparation process of the CuAl-Ni/C seal coating system, (b) NiAl clade powders, (c) CuAl-Ni/C clade powders and (d) as-sprayed CuAl-Ni/C seal coating system. (Image by IMR)
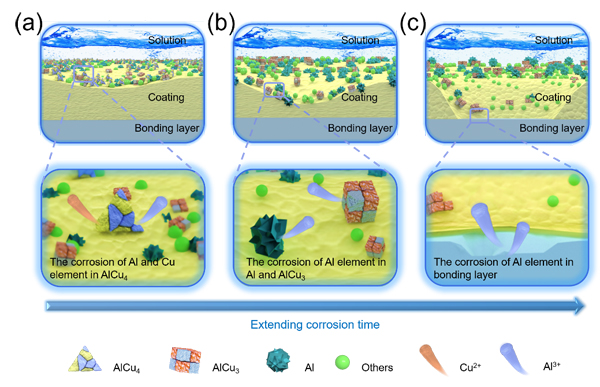
Figure 2. Schematic illustration of the anti-corrosive mechanism of the CuAl-Ni/C seal coating. (Image by IMR)