The hydrogenation of nitroarenes is an eco-friendly method for the production of anilines. For di-nitroaromatics hydrogenation, it is a challenge to achieve the multi-step hydrogenation reaction with high activity and selectivity as the presence of two nitro groups requires a rather complicated process. As a result, many conventional precious metal catalysts suffer from low activity and metal utilization in the multi-step hydrogenation. Hence, it is essential to develop efficient catalysts with high activity and selectivity, high metal utilization, and low cost for this multi-step hydrogenation reaction.
Recently, Prof. LIU Hongyang and his research team from Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. MA Ding from Peking University etc., have developed a novel strategy to design and synthesize highly efficient fully exposed Pt clusters catalysts for multi-step hydrogenation reactions. This work was published in Nature Communications.
In this work, the researchers fabricated a fully exposed Pt clusters catalyst (Ptn/ND@G) consisting of an average of four Pt atoms with the maximum atom utilization on a defect-rich nanodiamond@graphene supports for the complex multi-step hydrogenation. Ptn/ND@G showed an excellent catalytic activity under room temperature: high TOF (40647 h?1), high yield (>99%), and good stability (5 cycles), which is better than Pt single atoms catalysts, Pt nanoparticles catalysts, and even all other known catalysts. Moreover, Ptn/ND@G exhibited excellent catalytic performance for the multi-step hydrogenation of di-nitroarenes with different substitutional groups.
In-situ DRIFTS and DFT calculations indicate that the synergistic interaction between of fully exposed Pt clusters is beneficial to improve the co-adsorption of reactants and H2, as well as the desorption of intermediates/products, resulting in the excellent catalytic performance for this multi-step hydrogenation reaction. These findings open a new avenue for the design and development of novel catalysts for multi-step hydrogenation.
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFA1504500, 2022YFB4003100, 2021YFA1502802), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22072162, 2202213, 92145301, U21B2092, 21961160722, 91845201), the International Partnership Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (172GJHZ2022028MI), Shenyang Young Talents Program (RC210435), Dalian National Lab for Clean Energy (DNL Cooperation Fund 202001) and China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (No. 420043-2). The XAS experiments were conducted in Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility (BSRF) and Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF).
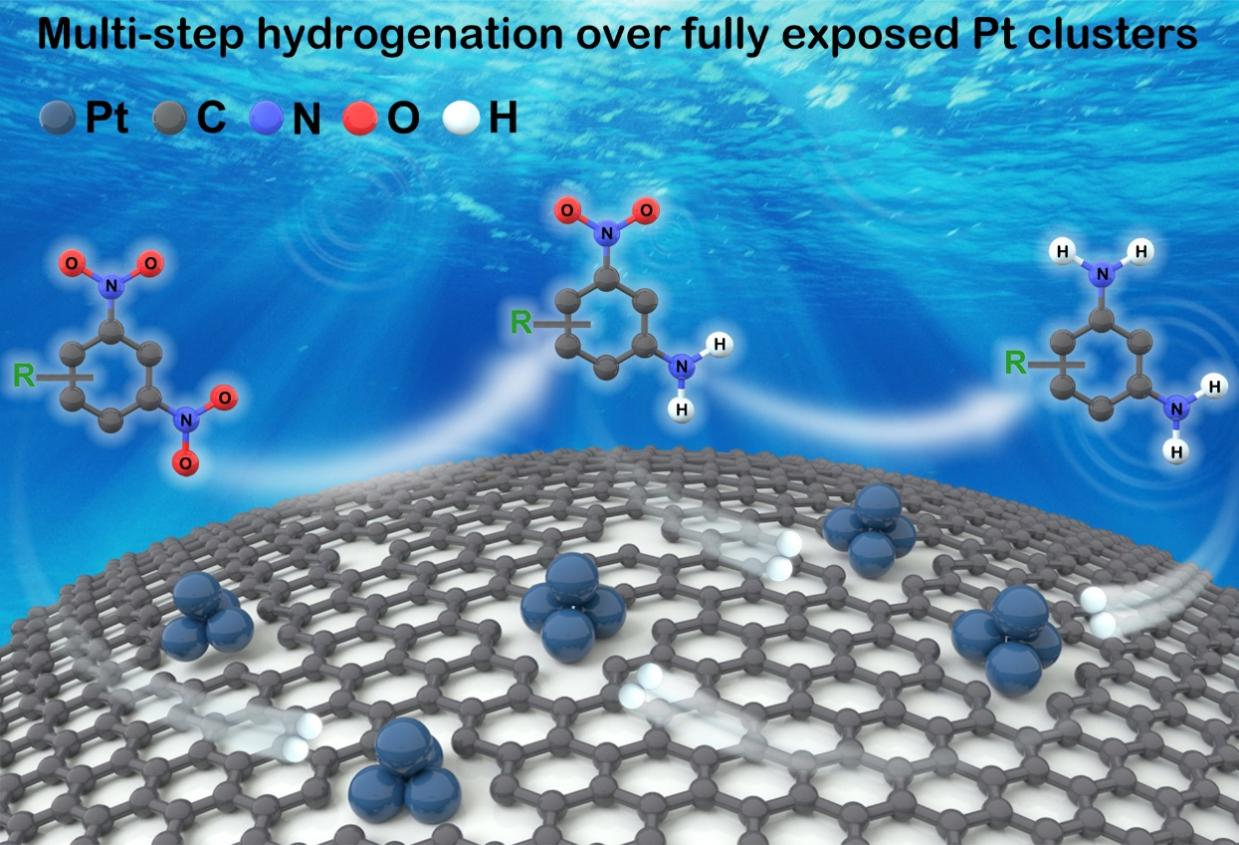
Schematic diagram of the multi-step hydrogenation of 2,4-DNT catalyzed by fully exposed Pt clusters catalyst.(Image by IMR)