Ferroelectrics tend to spontaneously form polydomain structures to minimize electrostatic energy. Nevertheless, single-domain thin films can be achieved through precise control of interfacial atomic layers or strain gradients. The quest for a simple method to obtain single-domain and its impact on the ferroelectric device performance are of great interest.
A research team led by Prof. Hu Weijin from the Institute of Metal Research (IMR) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has proposed that simply elevating the growing temperature can produce single-domain in ferroelectric thin films efficiently.
The team demonstrated that the ferroelectric single-domain, compared to polydomain, can significantly improve the ferroelectric synaptic devices performance.
This work was published in Advanced Functional Materials.
The team utilized BaTiO3 (BTO) ferroelectric films, which were deposited on top of La0.67Sr0.33MnO3 metallic layers at temperatures ranging from 700 oC to 850 oC using pulsed laser deposition, a technique well-suited for producing high-quality single- crystalline oxide films.
The researchers discovered that when LSMO was grown at temperatures above 800 oC, the BTO films exhibited a single-domain configuration. They observed that Sr ions tended to diffuse towards the interface, creating a positively charged surface that aligned the polarizations uniformly across the film.
“This approach is much simpler compared to other methods such as atomic layer engineering, which typically requires complex surface treatments and precise growth control,” said HU. “It holds the potential for large-scale production of single-domain films beyond the current 5 mm by 5 mm size, possibly through industrial processes like spin coating.”
Large-scale single-domain film could not only enhance the ferroelectric synapse performance used for neuromorphic computing, but also have applications in many other fields, including optoelectronics and catalysis.
The study was conducted in collaboration with scientists from IMR and South China Normal University.
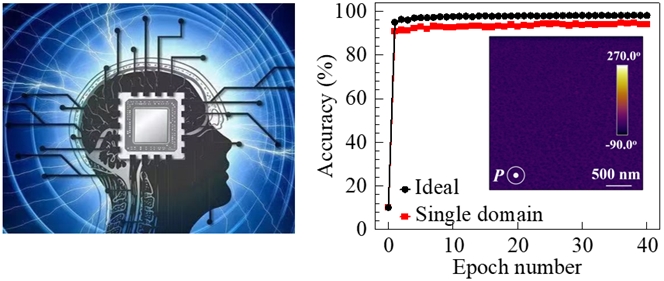
The conception of neuromorphic computing (left from Baidu) and pattern recognition accuracy of a single domain ferroelectric synapse (Image from IMR)
Key Words:
Nanovoids; Dispersion strengthening; Ductility: Lightweight material
Full Text:https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adfm.202423225