Brief Introduction
Catalysis is one of the core technologies in modern chemistry and energy industry, and over 60% of the chemical synthesis process involves catalytic material and techniques. Catalytic material is a substance that can adjust and optimize reaction kinetics or selectivity. The development of catalytic material is a powerful impetus for exploiting new energy, treating and controlling pollution, and synthesizing fine chemicals and medicines. In situ observations of and research on the mechanism of reactions between reactants and catalysts at the molecular or atomic level are the essential premise of the development of a new generation of highly effective, energy-saving, and environmentally friendly catalytic materials. The research effort of CMD focuses on the development of novel practical catalysts with unique and intriguing functionalities. According to the requirement of modern scientific development and national strategic needs, the research goal of CMD includes the synthesis and fabrication of new catalysts, in situ characterization and evaluation of catalysts, simulation and optimization of the catalytic process, and industrial applications for catalytic systems. Our specific research interest covers the highly efficient energy conversion of coal or nature gas, low-energy catalytic techniques, non-noble metallic catalysis, the development of new sustainable clean energy, natural catalytic materials, the remediation of air and soil contamination, the calculation and simulation of key catalytic systems, and in situ characterization of nano catalytic materials.
Research Areas
1) Physical Chemistry of the Reaction Catalyzed by Metal or Noble Metal Alternatives
2) Basic Research on Carbon and Nano Carbon
3) Exploitation of Industrial Applications of Carbon and Nano Carbon Catalysts
4) Fundamental Research on Shaping and Batch Production of Carbon and Nano Carbon Catalysts
5) Microscopic and In Situ Characterization of Nano Catalysts
6) Development of Novel Energy Storage Materials
Research Highlights
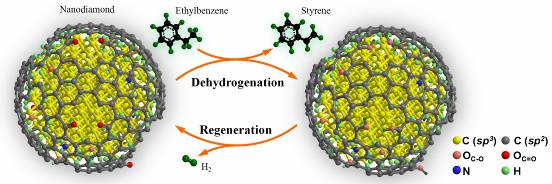
Schematic description of nanodiamond-catalyzed dehydrogenation process.
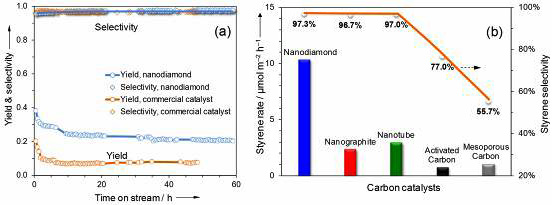
Results of catalytic evaluation and in situ characterization of nanodiamond. (a) Steam-free dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene at 550°C. Conditions: 50 mg catalyst, 2.8% ethylbenzene in helium, 10 mL/min gas flow rate, 1 atm. (b) In situ synchrotron-excited XPS spectra of nanodiamond under vacuum and ethylbenzene vapor at 400-450°C.